Robust Speech Recognition via Large-Scale Weak Supervision
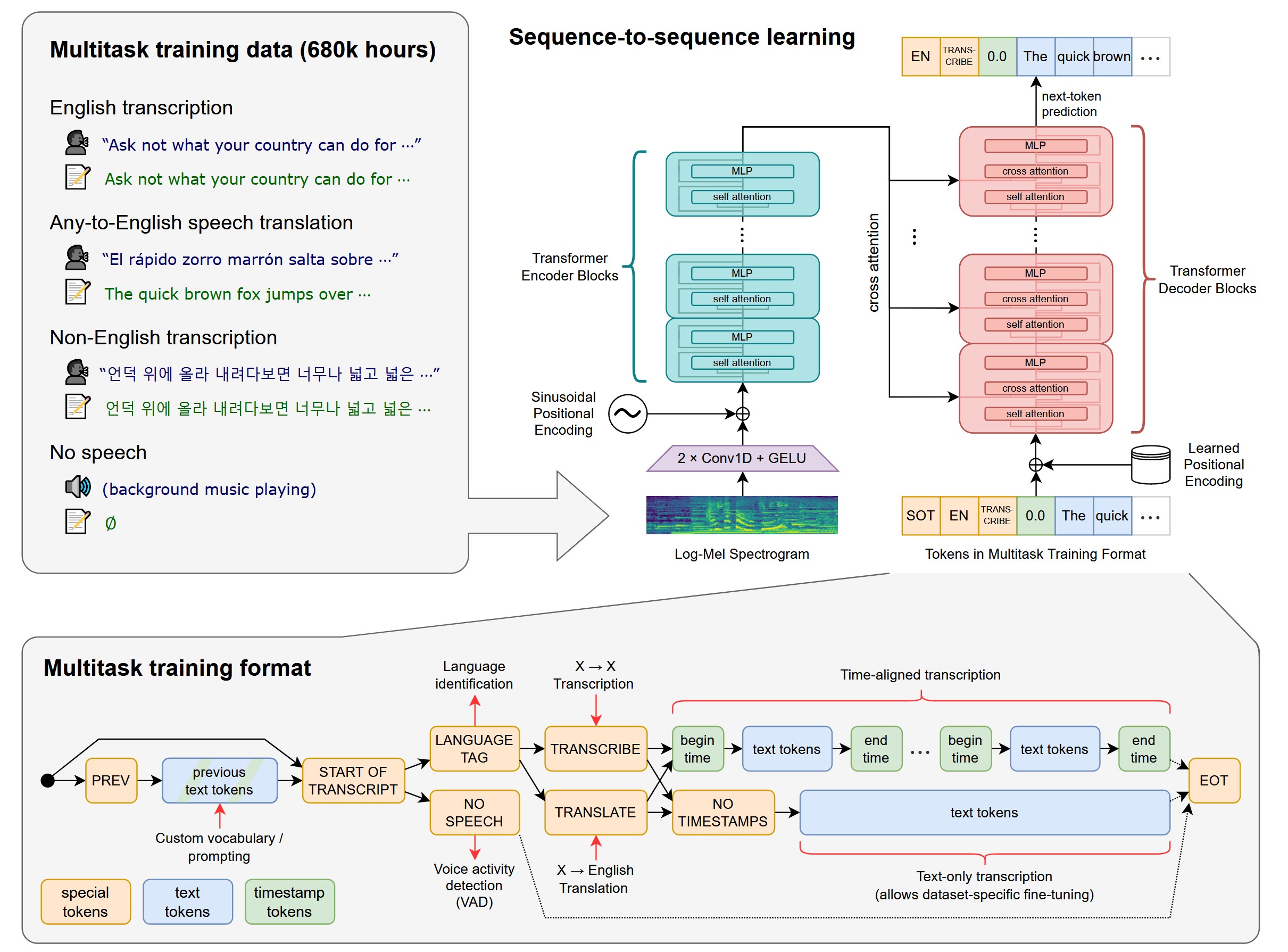
We study the capabilities of speech processing systems trained simply to predict large amounts of transcripts of audio on the internet. When scaled to 680,000 hours of multilingual and multitask supervision, the resulting models generalize well to standard benchmarks and are often competitive with prior fully supervised results but in a zeroshot transfer setting without the need for any finetuning. When compared to humans, the models approach their accuracy and robustness. We are releasing models and inference code to serve as a foundation for further work on robust speech processing.
Tokenizer
tiktoken库